Tests Reports
Video Tutorial: How to set up test reports
Test reports show a unified view of all your tests in a pipeline. This page explains how to configure test reports and interpret the test dashboard.
Overview
The test tab in your project offers a unified view of the state of tests across all your pipelines. The test reports dashboard highlights test failures and can be filtered in many ways to provide insights into your test suite.
How to set up test reports
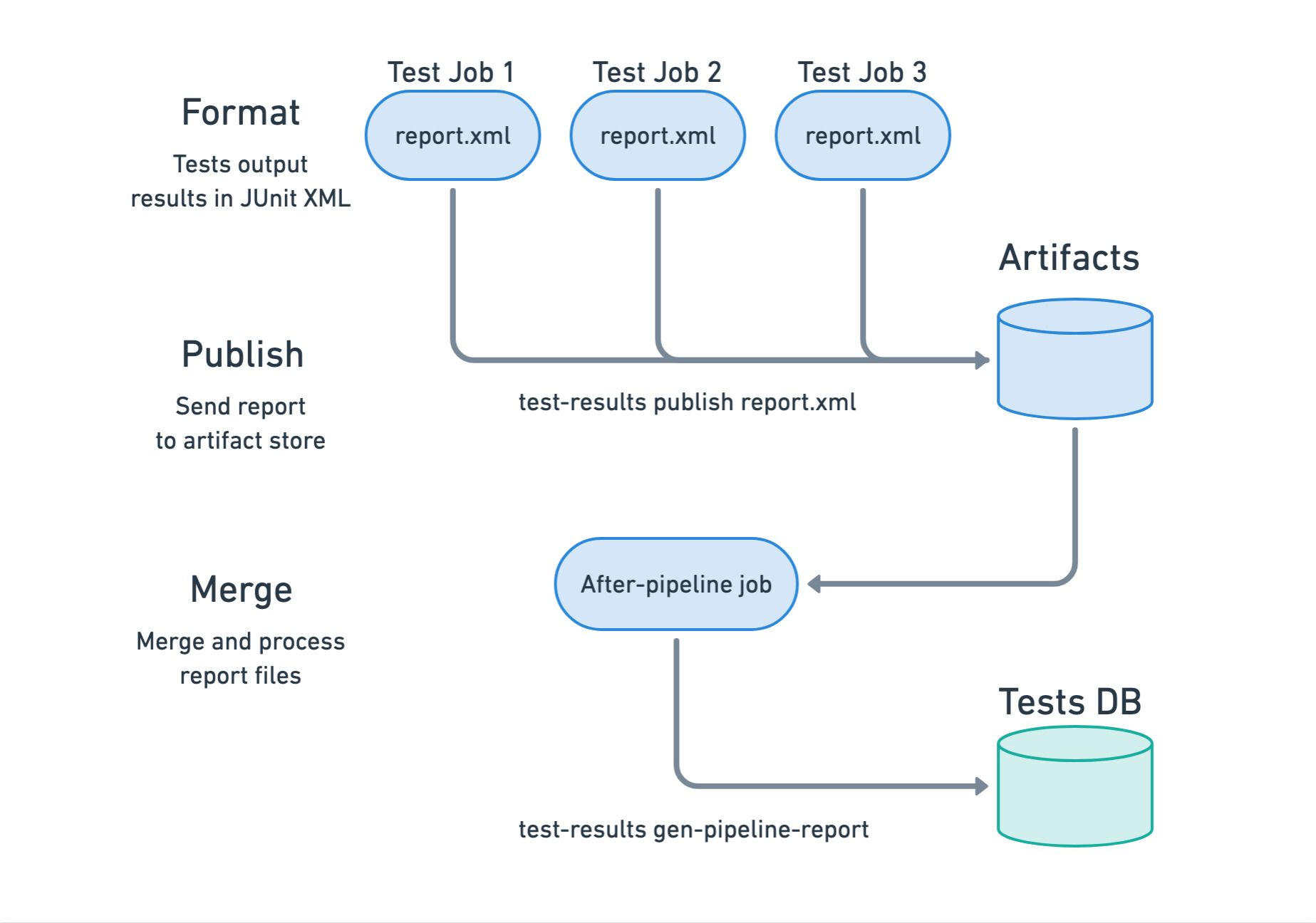
Before you can view your tests in the Test tabs, you need to perform a one-time setup. The benefit of having all tests in one place is usually worth the effort of this setup.
- Format: format test results in JUnit XML
- Publish: push results file into the artifact store
- Merge: collect and process all result files
Once test reports are configured, flaky test detection feature is automatically enabled.
Step 1 - Format
The JUnit XML format was created by the JUnit Project for Java but has been so popular that many other frameworks in diverse languages have implemented it.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<testsuites tests="3" failures="2" errors="0" time="0.850294">
<testsuite tests="3" failures="2" time="0.063000" name="github.com/semaphoreci-demos/semaphore-demo-go" timestamp="2024-05-27T22:14:24Z">
<properties>
<property name="go.version" value="go1.22.3 linux/amd64"></property>
</properties>
<testcase classname="github.com/semaphoreci-demos/semaphore-demo-go" name="Test_count" time="0.020000">
<failure message="Failed" type="">=== RUN Test_count
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
 main_test.go:84: Select query returned 0
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
--- FAIL: Test_count (0.02s)
</failure>
</testcase>
<testcase classname="github.com/semaphoreci-demos/semaphore-demo-go" name="Test_record" time="0.000000">
<failure message="Failed" type="">=== RUN Test_record
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
Serving: /getdata
Served: 
 main_test.go:144: Wrong server response!
dial tcp [::1]:5432: connect: connection refused
--- FAIL: Test_record (0.00s)
</failure>
</testcase>
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
The first step is to configure your test runner to generate a JUnit report. The format command runs as another command in the job — usually near the end.
To make setup easier, it's recommended to save all report files to the same path and filename. We'll use report.xml for the rest of the document.
Below there are examples of generating reports in different test runners.
Ruby on Rails example
To generate JUnit reports on Ruby on Rails projects we need to add the rspec_junit_formatter Gem:
group :development, :test do
# ...
gem "rspec_junit_formatter"
end
After running bundle install, we need to tell RSpec to use the new formatter. We can do this by extending the .rspec configuration file:
--format RspecJunitFormatter
--out report.xml
--format documentation
Alternatively, we can change the configuration via command line arguments:
bundle exec rspec --format RspecJunitFormatter --out report.xml --format documentation
Either way should generate a report.xml file at the root of the project.
Go example
Elixir example
To generate JUnit reports for your Elixir project, follow these steps:
-
Add junit-formatter to your
mix.exsmix.exsdefp deps do
[
# ...
{:junit_formatter, "~> 3.1", only: [:test]}
]
end -
Install the dependencies:
mix deps.get -
Extend your
config/test.exsconfig/test.exsconfig :junit_formatter,
report_dir: "/tmp",
report_file: "report.xml",
print_report_file: true,
include_filename?: true,
prepend_project_name?: false,
include_file_line?: true -
Extend your
test/test_helper.exstest/test_helper.exsExUnit.configure(formatters: [JUnitFormatter, ExUnit.CLIFormatter])
ExUnit.start() -
Run the tests. This should generate
report.xmlmix test
mv /tmp/report.xml .
The table shows possible test runners for popular languages. If your test runner is not listed here, you can still use test reports, but you need to find a test formatter that can export results to JUnit XML.
| Language | Test Runner | Formatter |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | Mocha | mocha-junit-reporter |
| JavaScript | Karma | karma-junit-reporter |
| JavaScript | ESLint | built-in |
| JavaScript | Jest | jest-junit |
| Ruby | RSpec | rspec_junit_formatter |
| Ruby | Cucumber | built-in |
| Elixir | ExUnit | junit-formatter |
| Go | GoTestSum | built-in |
| PHP | PHPUnit | built-in |
| Python | PyTest | built-in |
| Bash | Bats | built-in |
| Rust | Cargo Test | junit-report |
| Java | Maven | maven-surefire |
Step 2 - Publish
The publishing step uploads all report files to the artifact store. This is accomplished using the test-results tool, which is part of the Semaphore toolbox.
Assuming the file is called report.xml, you can publish the report with the following command.
[[ -f report.xml ]] && test-results publish report.xml
To simplify this step, you can add a pipeline epilogue to run the publish command after every job ends.
- Editor
- YAML
-
Select the pipeline with the test jobs
-
Add the publish command in the "Execute always" box of the Epilogue
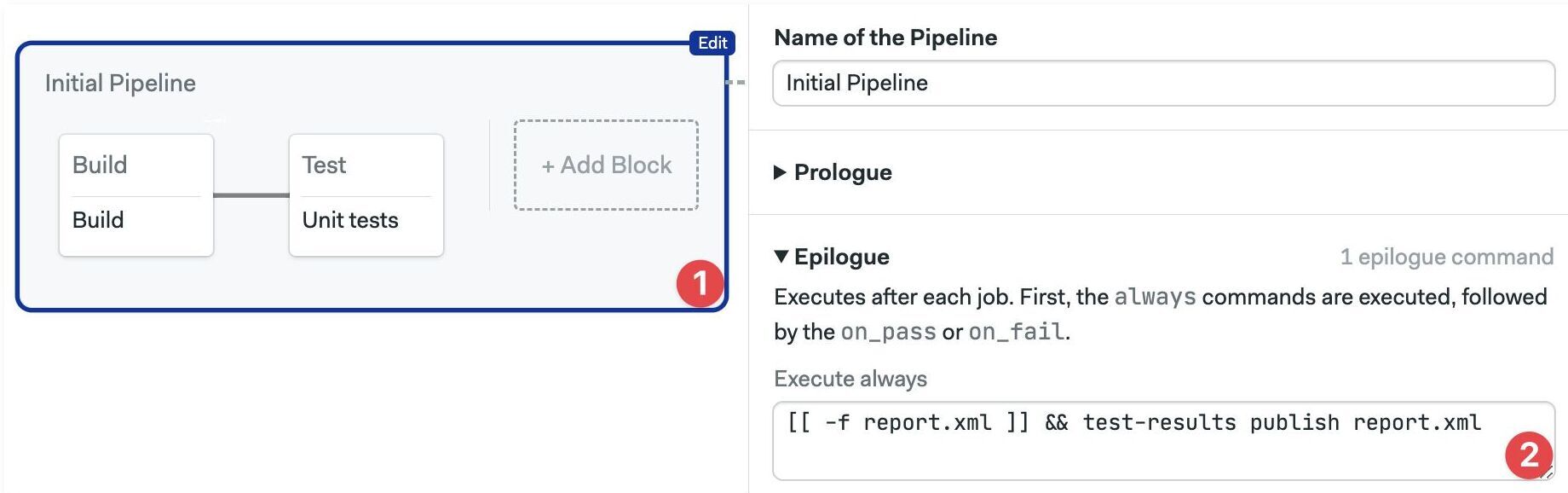
- Open the pipeline file with the test jobs
- Add a
global_job_configkey at the YAML root - Type the publish command under
epilogue.always.commands
# ...
global_job_config:
epilogue:
always:
commands:
- '[[ -f report.xml ]] && test-results publish report.xml'
Step 3 - Merge
The final step is to merge and process all report files. This is achieved using an after-pipeline job.
- Editor
- YAML
-
Press +Add After Jobs
-
Type a name for the job
-
Type the command
test-results gen-pipeline-report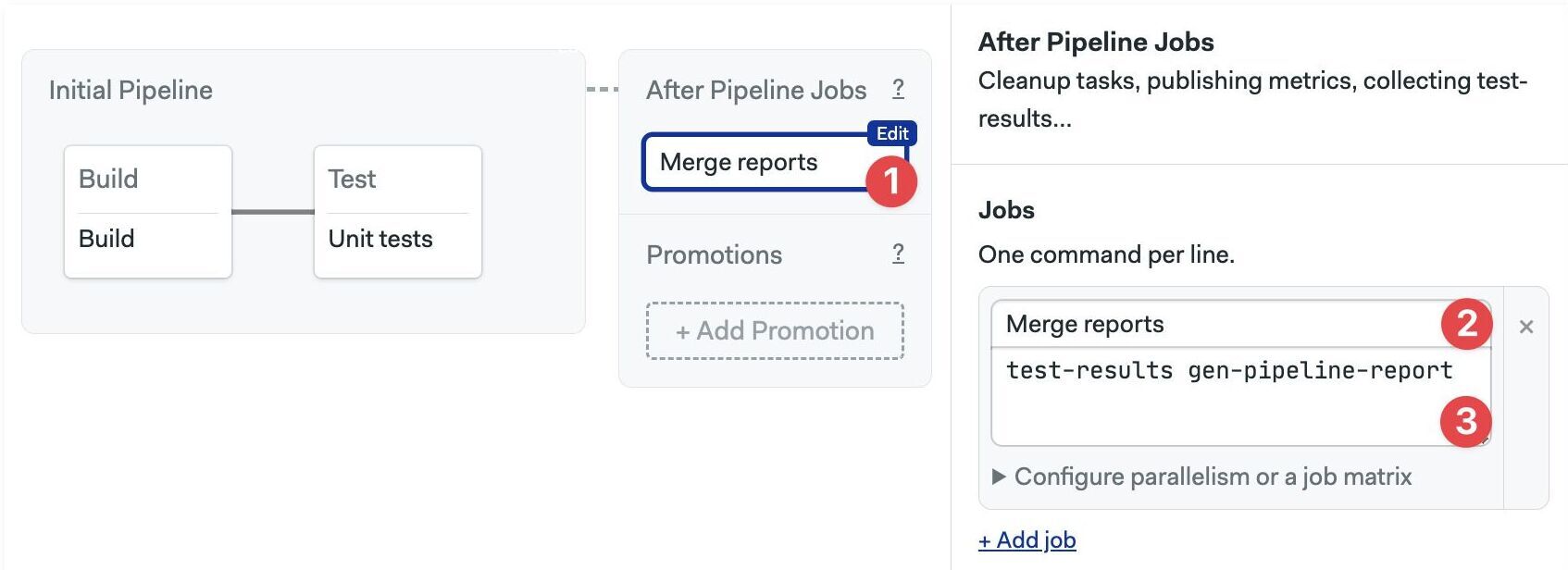
- Open the pipeline with the test jobs
- Add an
after_pipelinekey at the YAML root - Add the
nameundertask.jobs - Type the merge command
test-results gen-pipeline-reportin thecommandssection
# ...
after_pipeline:
task:
jobs:
- name: Merge reports
commands:
- test-results gen-pipeline-report
How to view test reports
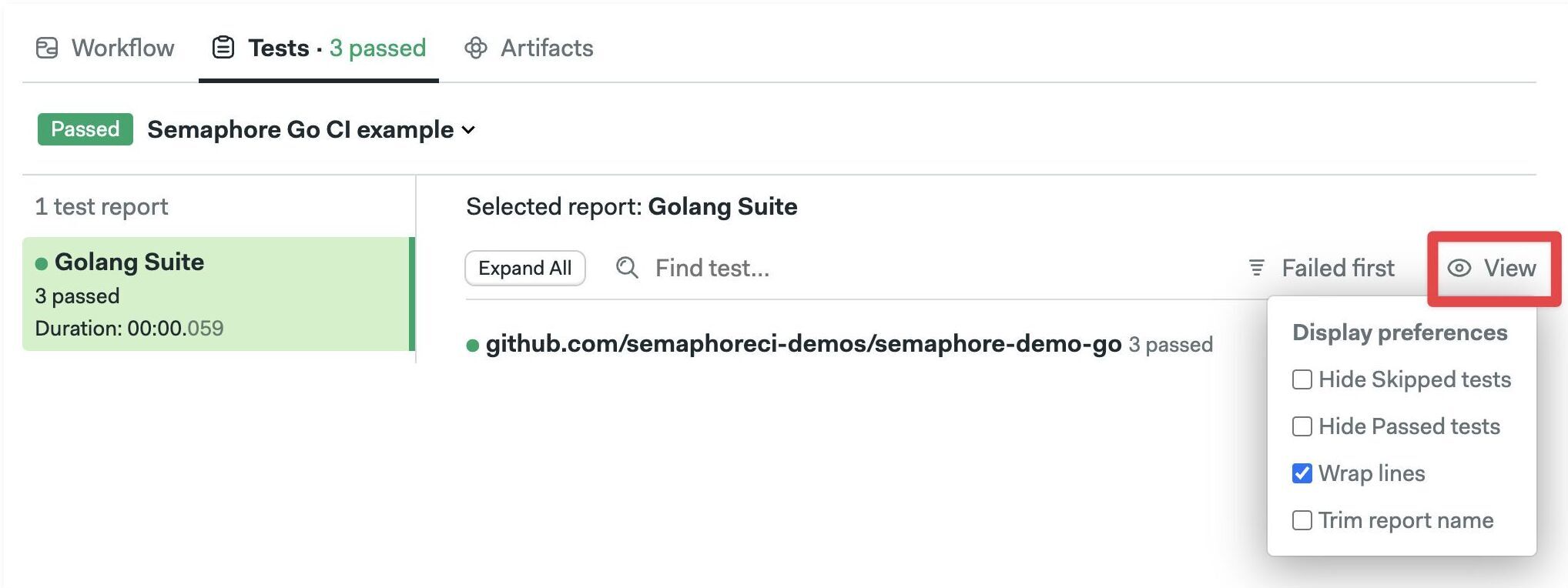
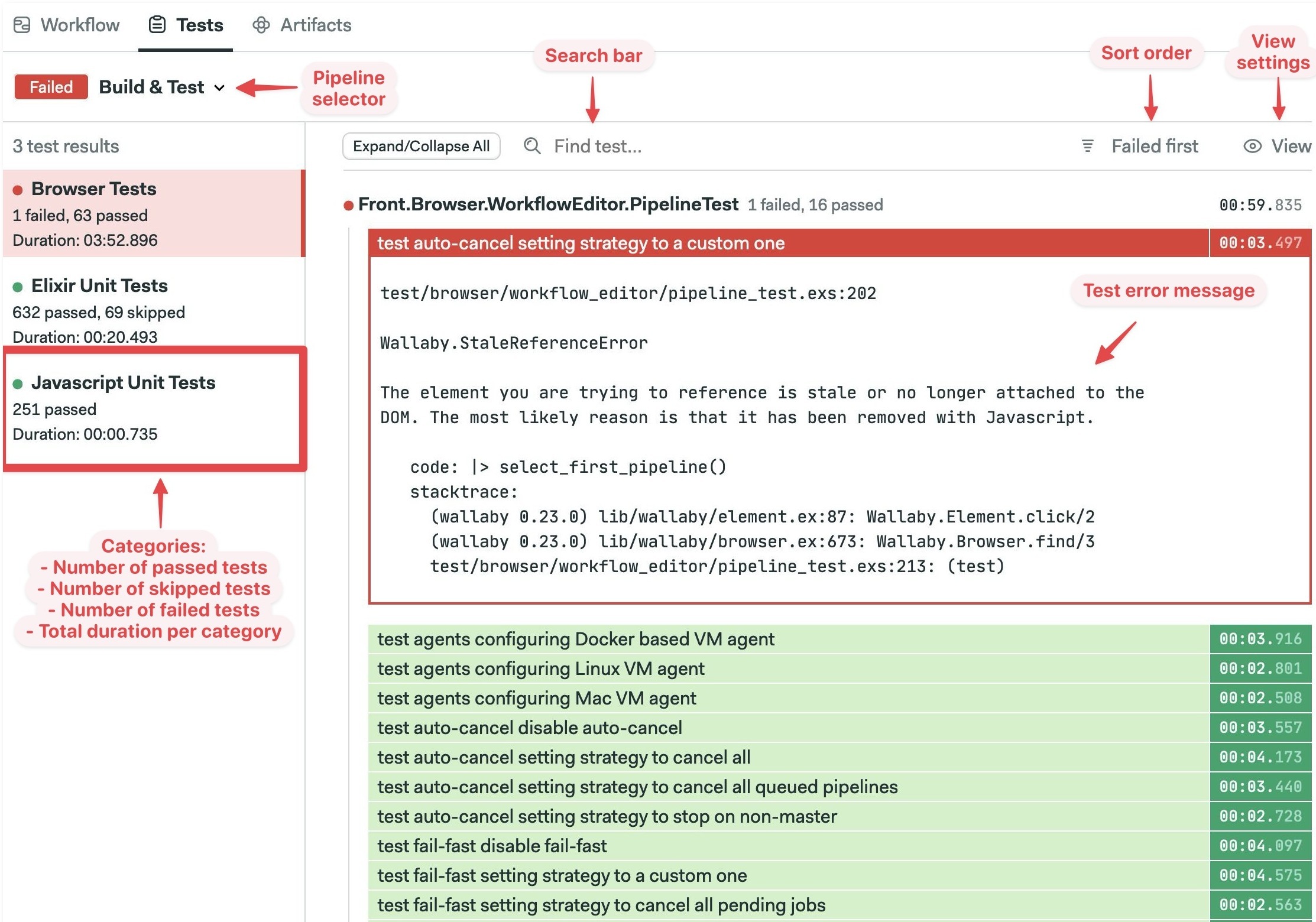
To view test results, navigate to your pipeline and go to the Tests tab.
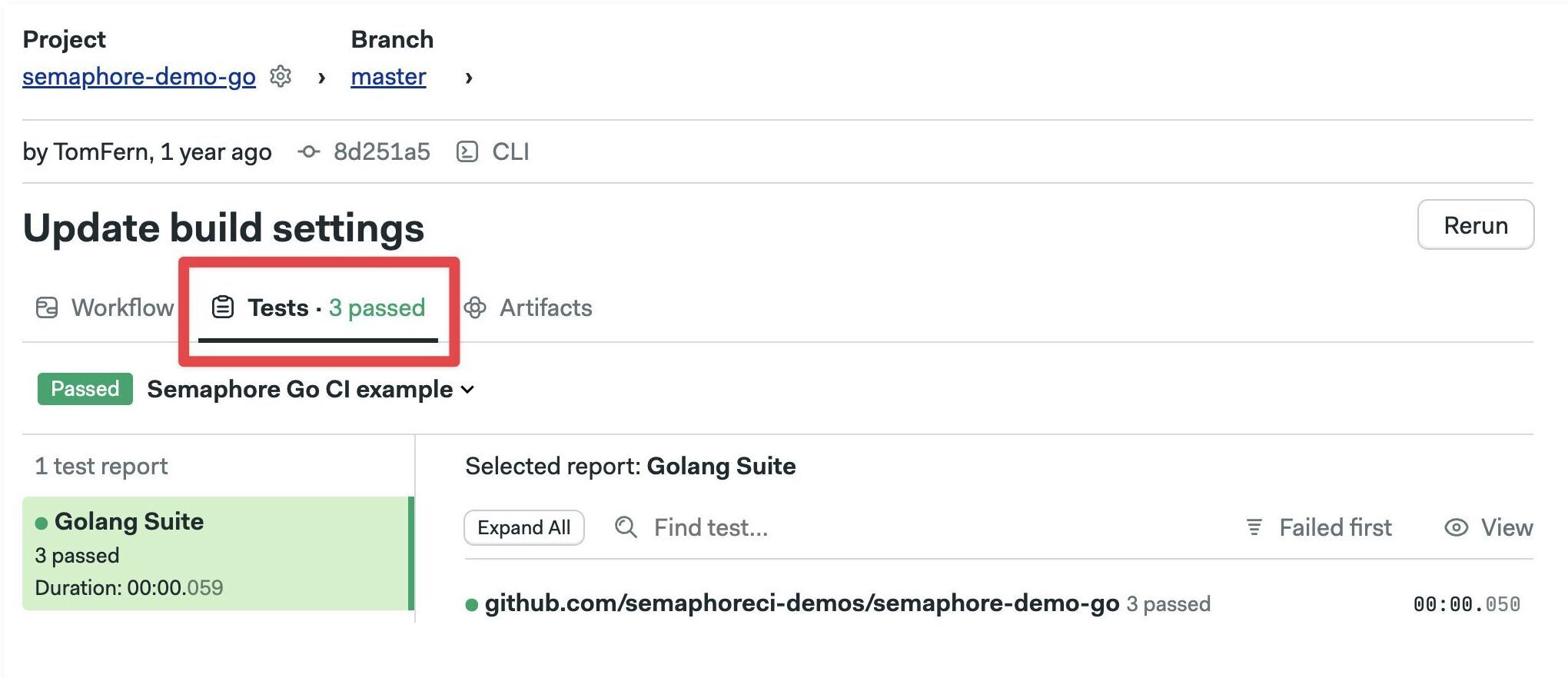
The test tab is only populated for the pipelines where test reports are configured. If you don't see anything yet, try rerunning the pipeline.
The default Test view shows failed tests first.
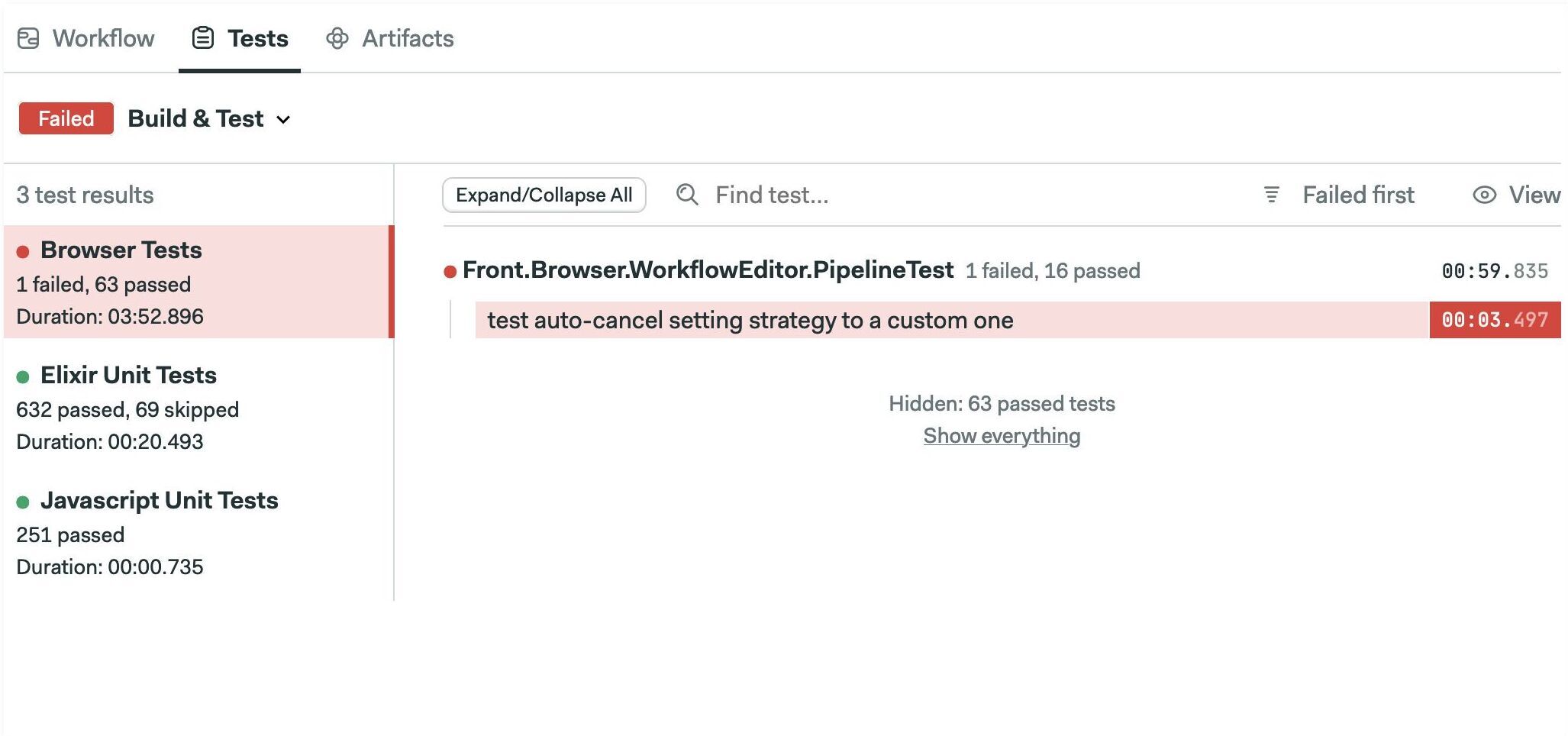
Click on "Failed first" to change the sort order. You can sort by "Slowest first" or alphabetically.
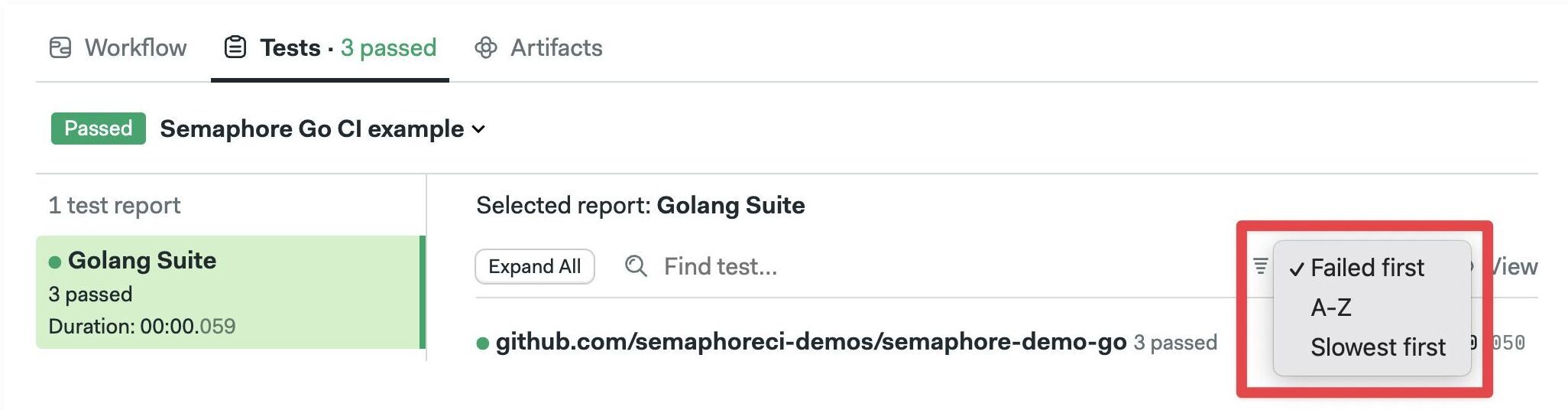
Click on "View" to change display preferences. You can hide passed or skipped tests and change how the report looks.