CircleCI
This page explains the core concepts and feature mapping you need to migrate from CircleCI to Semaphore.
Overview
CircleCI uses a YAML-based syntax to define pipelines and actions. With Semaphore, in addition to this method, you can also use the visual workflow editor to easily configure and preview pipelines.
Semaphore provides top-of-market machines for faster build times, along with extra features like fully customizable Role Based Access Control, parameterized promotions, and SSH debugging.
CircleCI vs Semaphore
This section describes how to implement common CircleCI functionalities on Semaphore.
Checkout
Checkout clones the repository in the CI environment.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI uses the Checkout action in every step and job that requires a copy of the repository.
jobs:
my_job:
docker:
- image: cimg/base:current
steps:
- checkout
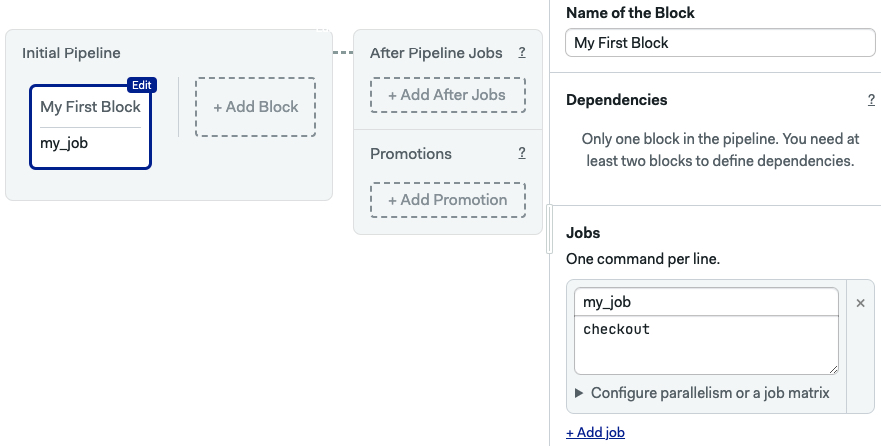
To clone the repository on Semaphore, execute checkout.
jobs:
- name: my_job
commands:
- checkout
In addition, by using prologue and global_job_config you can declare the checkout for all jobs.
global_job_config:
prologue:
commands:
- checkout
Language versions
Both CircleCI and Semaphore allow you to use specific language versions.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI uses a language-specific setup orb.
The following example sets the Ruby version to 3.3.4
version: 2.1
orbs:
ruby: circleci/ruby@x.y
jobs:
my_job:
docker:
- image: cimg/base:current
steps:
- ruby/install:
version: '3.3.4'
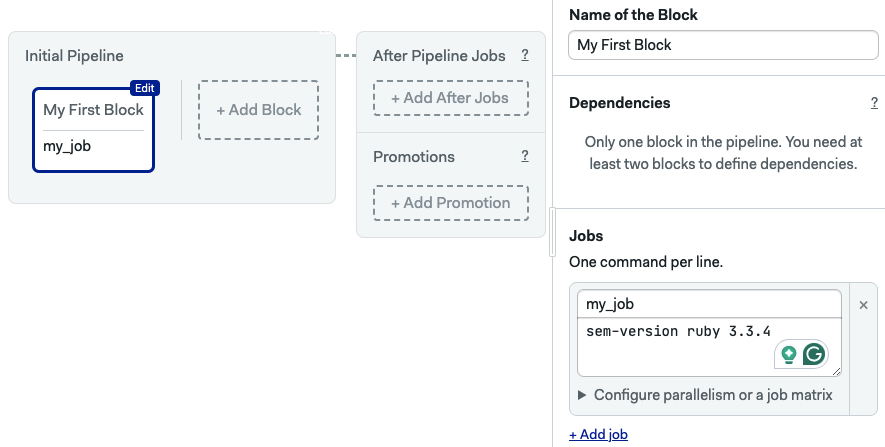
Semaphore uses sem-version to activate or switch language versions in the CI environment.
The following example activates Ruby v3.3.4, any commands after the example run on this Ruby version.
jobs:
- name: my_job
commands:
- sem-version ruby 3.3.4
Caching
Both CircleCI and Semaphore support manual file caching.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI has a cache action to cache files. The following example caches Gems in a Ruby project:
- restore_cache:
name: Restore Ruby Cache
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
- run: bundle install --deployment --path vendor/bundle
- save_cache:
name: Save Ruby Gems
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
paths:
- vendor
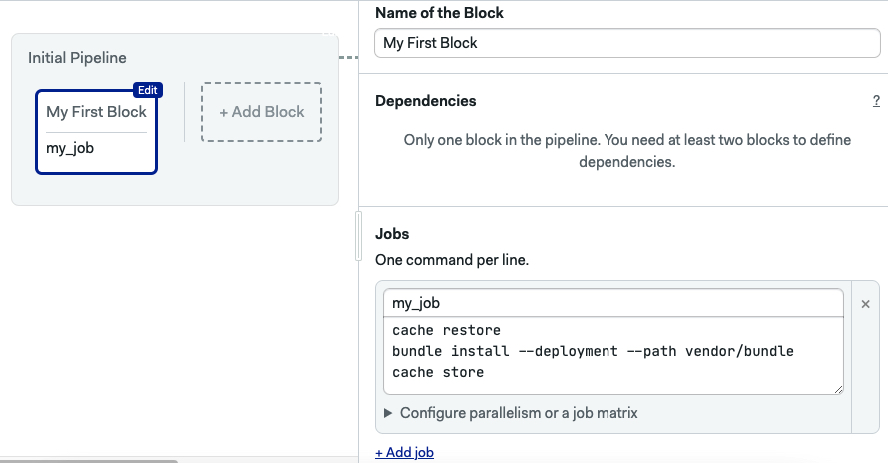
Semaphore uses the cache command to cache dependencies and files.
The following commands, when added to a job downloads, cache, and install Gems in a Ruby project:
- name: Cache gems
commands:
- cache restore
- bundle install --deployment --path vendor/bundle
- cache store
See caching for more details.
Database and services
Both CircleCI and Semaphore support starting databases and services via Docker containers.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI uses service containers. The following example starts service containers for both Postgres and Redis.
jobs:
my_job:
docker:
- image: cimg/base:current
environment:
REDIS_URL: redis://redis:6379
- image: cimg/postgres:16.0
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
- image: cimg/redis:5.0
On Semaphore, we use sem-service to start and stop services in the CI environment.
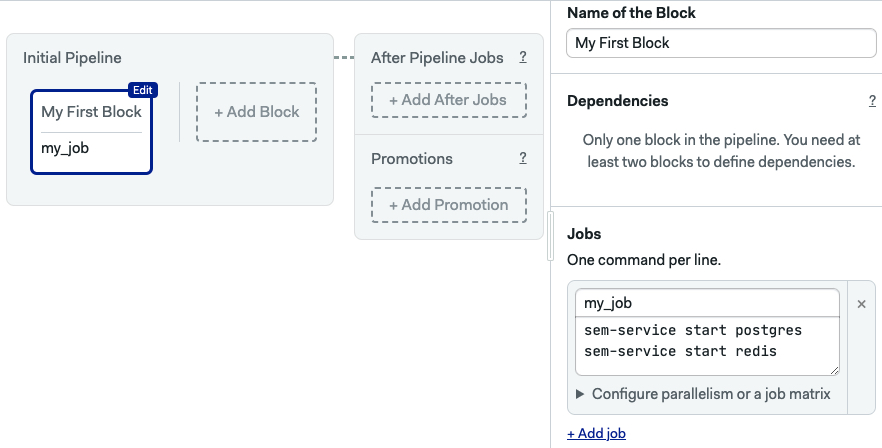
The following example starts Postgrest and Redis on the default port (6379).
jobs:
- name: my_job
commands:
- sem-service start postgres
- sem-service start redis
Artifacts
Both CircleCI and Semaphore support persistent Artifacts storage.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI uses the actions store_artifacts to upload and the API to download artifacts.
The following example uploads and downloads test.log
- store_artifacts:
path: /tmp/test.log
# Downloading artifacts
- run: curl -H "Circle-Token: <circle-token>" https://circleci.com/api/v1.1/project/:vcs-type/:username/:project/latest/artifacts
Semaphore uses the artifact command to download and upload files to the artifact store.
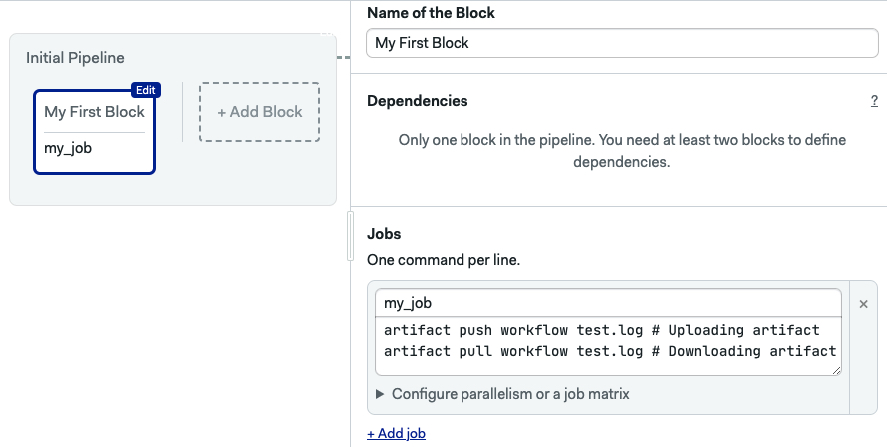
The following command stores test.log from any job:
jobs:
- name: my_job
commands:
- artifact push workflow test.log
To retrieve the file from any other job, use:
jobs:
- name: my_job
commands:
- artifact pull workflow test.log
See artifacts for more details.
Secrets
Secrets inject sensitive data and credentials into the workflow securely.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
CircleCI uses contexts instead of secrets. You must create the context and its value through the UI.
Then, you can use the context keyword to include it in your jobs.
workflows:
my_workflow:
jobs:
- my_job:
context:
- awskey
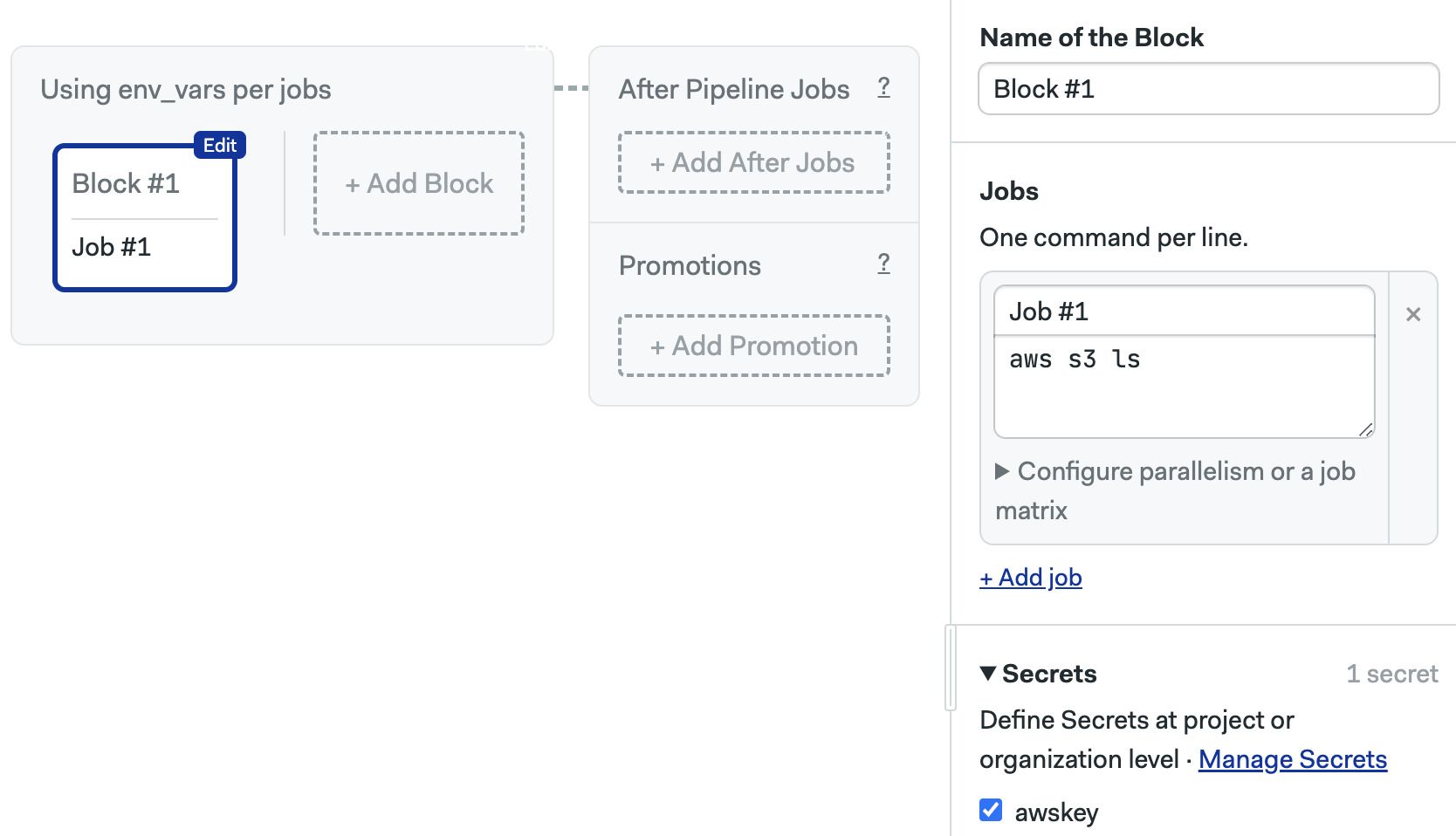
On Semaphore, we create the secret at the organization or project level and activate it on a block.
The secret's contents are automatically injected as environment variables in all jobs in that block.
blocks:
- name: Test
task:
secrets:
- name: awskey
Additionally, it's possible to connect secrets to all jobs in the pipeline by using global_job_config.
global_job_config:
secrets:
- name: awskey
On Semaphore, we create the secret at the organization or project level and activate it on a block.
The secret's contents are automatically injected as environment variables in all jobs in that block.
Complete example
The following comparison shows how to build and test a Ruby on Rails project on CircleCI and Semaphore.
- CircleCI
- Semaphore YAML
- Semaphore Editor
On CircleCI, we need several actions to start services, manage Gems, and run the build and test commands.
version: 2.1
jobs:
scan_ruby:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.3.5
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
name: Restore Ruby Cache
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
- run:
name: Set up Ruby
command: |
echo "Using Ruby version from .ruby-version"
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install --jobs=4 --retry=3
- save_cache:
name: Save Ruby Gems
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
paths:
- vendor
- run:
name: Scan for common Rails security vulnerabilities using static analysis
command: bin/brakeman --no-pager
scan_js:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.3.5-node
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
name: Restore Ruby Cache
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
- run:
name: Set up Ruby
command: |
echo "Using Ruby version from .ruby-version"
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install --jobs=4 --retry=3
- save_cache:
name: Save Ruby Gems
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
paths:
- vendor
- run:
name: Scan for security vulnerabilities in JavaScript dependencies
command: bin/importmap audit
lint:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.3.5
steps:
- checkout
- restore_cache:
name: Restore Ruby Cache
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
- run:
name: Set up Ruby
command: |
echo "Using Ruby version from .ruby-version"
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install --jobs=4 --retry=3
- save_cache:
name: Save Ruby Gems
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
paths:
- vendor
- run:
name: Lint code for consistent style
command: bin/rubocop -f github
test:
docker:
- image: cimg/ruby:3.3.5
- image: cimg/postgres:16.4.0
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
- image: cimg/redis:6.2.6
steps:
- run:
name: Install packages
command: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y curl libjemalloc2 libvips sqlite3
- checkout
- restore_cache:
name: Restore Ruby Cache
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
- run:
name: Set up Ruby
command: |
echo "Using Ruby version from .ruby-version"
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'
bundle install --jobs=4 --retry=3
- save_cache:
name: Save Ruby Gems
key: gems-v1{{ checksum "Gemfile.lock" }}
paths:
- vendor
- run:
name: Run Rake
environment:
RAILS_ENV: test
command: |
cp .sample.env .env
bundle exec rake db:setup
bundle exec rake
- run:
name: Run tests
environment:
RAILS_ENV: test
command: bin/rails db:test:prepare test test:system
workflows:
version: 2
main:
jobs:
- scan_ruby
- scan_js
- lint
- test
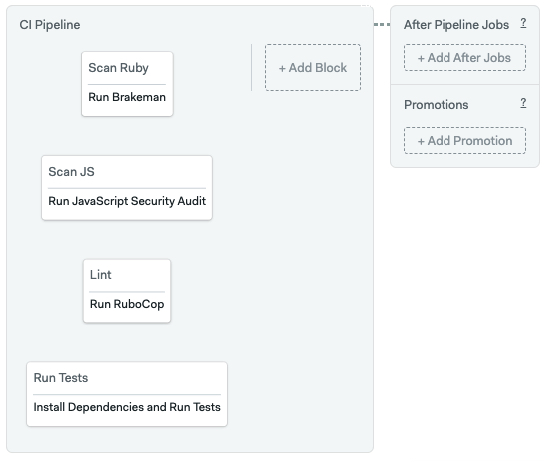
The following example runs the same CI procedure. You can optimize for speed by splitting the tests into different jobs.
version: v1.0
name: CI Pipeline
agent:
machine:
type: f1-standard-2
os_image: ubuntu2204
global_job_config:
prologue:
commands:
- checkout
- sem-version ruby $(cat .ruby-version)
- cache restore
- bundle install --jobs 4 --retry 3
- cache store
- sem-service start postgres
- sem-service start redis
blocks:
- name: Scan Ruby
task:
jobs:
- name: Run Brakeman
commands:
- bin/brakeman --no-pager
dependencies: []
- name: Scan JS
task:
jobs:
- name: Run JavaScript Security Audit
commands:
- bin/importmap audit
dependencies: []
- name: Lint
task:
jobs:
- name: Run RuboCop
commands:
- bundle exec rubocop -f github
dependencies: []
- name: Run Tests
task:
jobs:
- name: Install Dependencies and Run Tests
commands:
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y curl libjemalloc2 libvips sqlite3
- cp .sample.env .env
- 'bundle exec rake db:setup'
- bundle exec rake
- 'bin/rails db:test:prepare test test:system'
dependencies: []