Travis CI
This page explains the core concepts and feature mapping you need to migrate from Travis CI to Semaphore.
Overview
Travis CI is a YAML-based syntax to define pipelines and actions. In Semaphore, you can use the visual workflow editor to more easily configure and preview pipelines.
Semaphore cloud machines also provide a 2x speed boost and much better reliability when compared with Travis CI.
Travis CI vs Semaphore
This section describes how to implement common Travis CI functionalities in Semaphore.
Checkout
Checkout clones the repository in the CI environment.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
Checkout is implicit in all Travis CI workflows by default.
Semaphore does not clone the repository by default. This is because there are certain scenarios in which you don't need the code or you want to customize the cloning process.
To clone the repository in Semaphore we only need to execute checkout.
checkout
# now the code is the current working directory
cat README.md
Artifacts
Both Travis CI and Semaphore support a method to persist data between jobs called Artifacts.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
In Travis CI we use the artifacts addon.
The following example uploads and downloads test.log
addons:
artifacts:
paths:
- $HOME/project/test.log
Caching
Both Travis CI and Semaphore support manually caching files. See the comparison below.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
Travis CI has a cache keyword to cache files and dependencies.
The following example caches Gems in a Ruby project:
language: ruby
cache: bundler
Language versions
Both Travis CI and Semaphore allow you to use specific language versions.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
Travis CI uses a language-specific setup keyword.
The following example sets the Ruby version to 3.3.4
language: ruby
rvm:
- 3.3.4
Semaphore uses sem-version to activate or switch language versions in the CI environment.
The following example activates Ruby v3.3.4, any commands after the example run on this Ruby version.
sem-version ruby 3.3.4
Database and services
Both Travis CI and Semaphore support starting a databases and services. Semaphore uses Docker containers for this.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
Travis CI uses services keyword. The following example starts Redis on default port.
services:
- redis-server
On Semaphore, we use sem-service to start and stop services in the CI environment.
The following example starts Redis on the default port (6379)
sem-service start redis
Secrets
Secrets inject sensitive data and credentials into the workflow securely.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
In Travis CI we encrypt sensitive data using the Travis CLI. Travis uses asymmetric encryption to put the encrypted values in the YAML pipeline.
to access the values, we use the secure keyword, which tells Travis to decrypt the value on runtime.
env:
global:
- secure: "... long encrypted string ..."
Using encrypted files uses a different system that's a bit more convoluted.
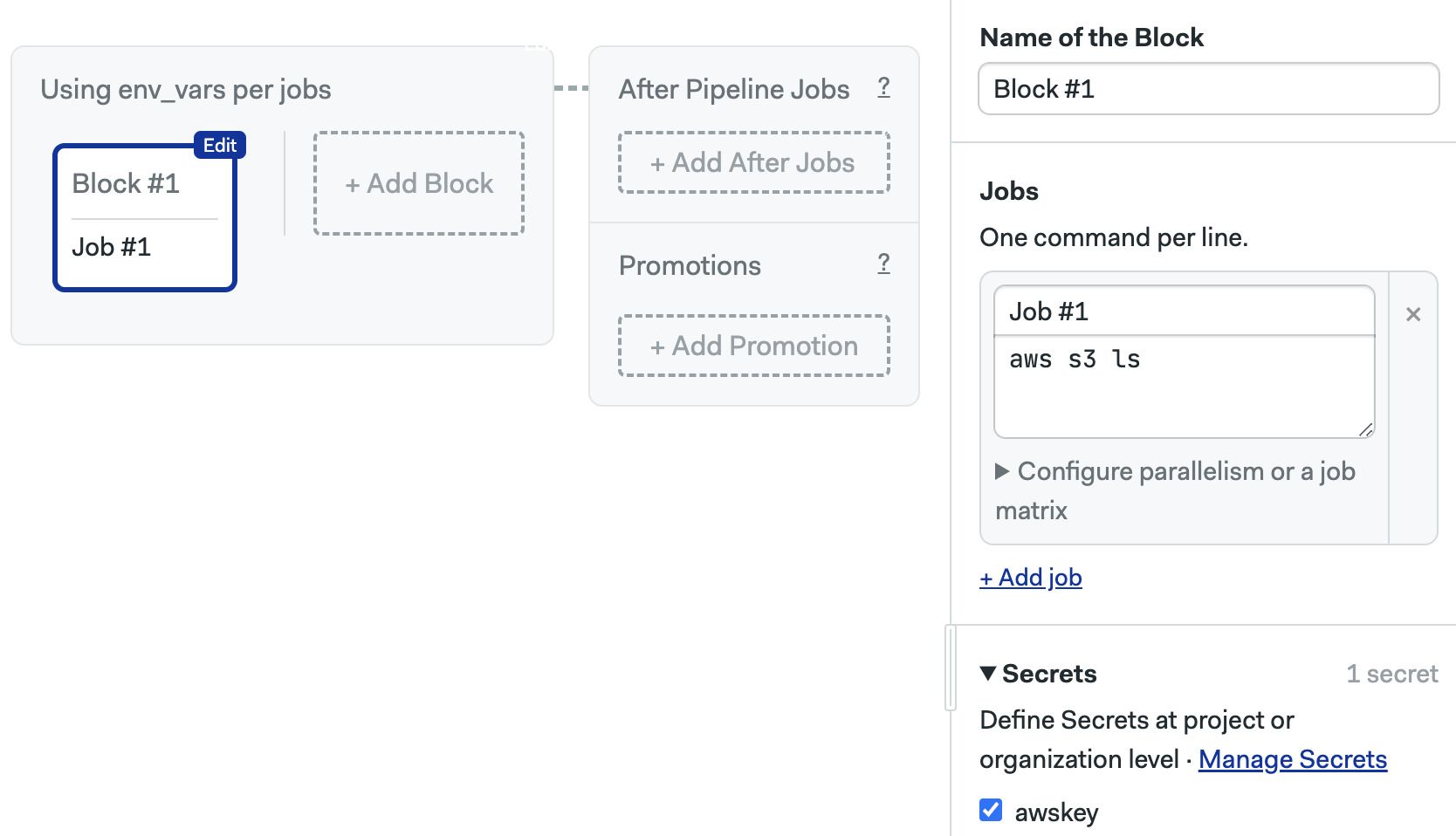
In Semaphore, secrets are stored on the Semaphore organization or project. Encryption and decryption is automatically handled for environment variables and files.
First, we create a secret at the organization or project level and activate it on a block.
The secret contents are automatically injected as environment variables in all jobs contained on that block.
Complete example
The following comparison shows how to build and test a Ruby project on Travis CI and in Semaphore.
- Travis CI
- Semaphore
On Travis CI, we need several actions to start services, manage Gems, and run the build and test commands.
language: ruby
rvm:
- $(cat .ruby-version)
cache: bundler
addons:
apt:
packages:
- curl
- libjemalloc2
- libvips
- sqlite3
branches:
only:
- main
jobs:
include:
- stage: security_scans
name: "Scan Ruby"
script:
- bin/brakeman --no-pager
- stage: security_scans
name: "Scan JS"
script:
- bin/importmap audit
- stage: lint
script:
- bin/rubocop -f github
- stage: test
before_script:
- cp .sample.env .env
- bundle exec rake db:setup
script:
- bundle exec rake
- bin/rails db:test:prepare test test:system
env:
global:
- RAILS_ENV=test
We can achieve the same results in a single job on Semaphore by using these commands:
checkout
sem-version ruby 3.3.4
sem-service start postgres
cache restore
nvm install --lts
bundle install --path vendor/bundle
yarn install
cache store
bundle exec rake db:create
bundle exec rake db:schema:load
bundle exec rake test
bundle exec rake test:system